

Longitude angles are also measured from the center of the Earth, 180 degrees east and west of the ~ running through the Royal Naval Observatory in Greenwich, England,9 a location fixed by international agreement in 1884. Because the lines of longitude converge at the poles, a degree of longitude represents a varying distance on the ground, depending on the latitude. Longitude increases as you move away from the ~, or 0°, in Greenwich, England. Longitude is the east or west location of a point, measured as an angle from the earth's center east or west of a ~, a given point on the earth's surface at 0 degrees longitude. Designed to help orient new players to the ethos of the geocaching community and to guide experienced players in questionable situations, so that everyone can enjoy geocaching. Creed, The Also known as the "Geocachers' Creed". The ~ runs through Greenwich, England near zero degrees longitude. On maps they are graded in degrees E and W from the ~. Moving from the ~, measures of longitude are negative to the west and positive to the east up to 180 degrees halfway around the globe. In a geographical coordinate system, it is a line of longitude defined to be 0°. The Greenwich meridian is a line of longitude that passes through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England. map projection conversion from a geodetic coordinate system to a planar surface ~. Geocentric coordinate reference system 3-dimensional coordinate reference system with its origin at the (approximate) centre of the Earth. 180° East and West longitude together form the International Date Line. Longitude specifies positions east and west as the angle be tween the ~ and a second meridian that intersects the point of interest. Being a reference line or origin for measuring angles, the ~ has a longitude of 0°. The longitude of a point on the surface of the earth is the angular distance (λ) east or west from a reference line called ~ that runs from North Pole to South Pole. The most commonly used ~ is the one running through Greenwich, England. ~ - the line running north-south along the Earth's surface indicating 0° longitude. The most common angular units used are decimal degrees (DD), degree minutes seconds (DMS), and decimal minutes (DM). While the equator divides Earth into Northern and Southern Hemispheres, it is the ~ at zero degrees longitude and the line of longitude opposite the ~ (near the International Date Line) at 180 degrees longitude that divides Earth into the Eastern and Western hemispheres. Meridian from which the longitudes of other meridians are quantified However, local or national ~s are occasionally used.
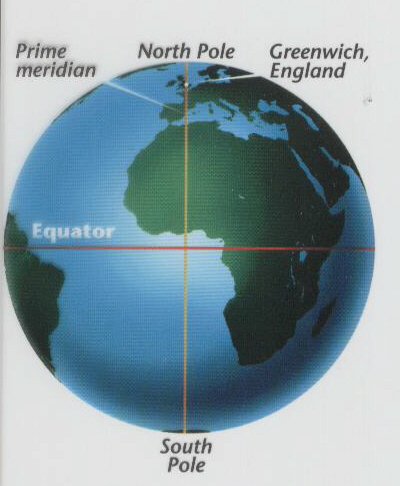
The meridian of Greenwich, England, is the internationally accepted ~ on most charts. ~: Meridian of longitude 0 degrees, used as the origin for measurements of longitude. ~ - Imaginary line that runs north to south through Greenwich, England dividing the earth into eastern and western hemispheres it also serves as the origin (0°) for the measurement of longitude.

Prime Meridian: The initial meridian or longitude 0 degree ( Greenwich Meridian), which creates the plane from which an angle is measured to establish the longitude of a point (see Longitude). An imaginary line running from north to south through Greenwich, England, used as the reference point for longitude.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
